When it comes to heating your home in an efficient, eco-friendly, and cost-effective way, wood-burning stoves are a popular choice. But choosing the right stove isn’t always straightforward. Each type of stove offers unique benefits, suited for different living situations, budgets, and design preferences. Let’s break down the five main types of wood-burning stoves in detail so you can make an informed decision.
1. Traditional Free-Standing Wood-Burning Stoves

| Key Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Heat Output | High, suitable for large spaces |
| Aesthetic Appeal | Variety of styles and finishes |
| Durable Build | Cast iron or steel for longevity |
Traditional free-standing wood-burning stoves are the most recognizable type, offering a high level of heating power. They can be placed almost anywhere with a chimney or venting system.
- Use Cases:
- Ideal for homes with open floor plans or larger spaces.
- Suitable for households seeking a centerpiece for both practical and aesthetic reasons.
- Installation Considerations:
- Space Requirements: Adequate floor space and clearance from walls and furniture.
- Chimney Installation: Necessary for safety, adding to the overall cost.
- Fire Codes and Safety Regulations: Meeting local codes, including heat shields and fire-resistant materials.
- Maintenance:
- Regular Cleaning: Prevent soot and ash buildup for efficiency and safety.
- Chimney Maintenance: Annual inspections to prevent creosote buildup.
Latest Development: The U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) has updated its emissions standards for new wood heaters, including free-standing stoves, aiming to reduce particulate matter emissions by 70% starting from May 2023.
2. Wood-Burning Stove Inserts

| Key Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Efficient Heat Use | Captures and distributes heat effectively |
| Design Flexibility | Range of sizes and designs to fit existing fireplaces |
| Ventilation | Requires proper venting through the chimney |
Wood-burning stove inserts transform underperforming fireplaces into efficient heating solutions.
- Use Cases:
- Perfect for homes with existing, inefficient fireplaces.
- Ideal for modernizing fireplaces without full renovation.
- Installation Considerations:
- Custom Fitting: Professional installation for a snug fit.
- Sealing the Fireplace: Ensuring no air leaks for improved efficiency.
- Maintenance:
- Chimney Care: Regular cleaning to prevent creosote buildup.
- Routine Stove Cleaning: Less frequent than open fireplaces.
Resource: Consult the National Fire Protection Association (NFPA) guidelines for safe installation and maintenance practices.
3. Pellet Stoves

| Key Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Automated Heating | Thermostats and automatic feed systems |
| Efficiency | Up to 80-90% efficiency, depending on the model |
| Cleaner Burn | Less smoke and ash compared to traditional wood stoves |
Pellet stoves offer an eco-friendly, efficient, and low-maintenance heating option.
- Use Cases:
- Perfect for those seeking efficient, low-maintenance heating.
- Ideal for eco-conscious homeowners.
- Installation Considerations:
- Electricity Requirement: Dependency on electricity for operation.
- Pellet Supply: Ongoing cost for pellet fuel.
- Maintenance:
- Ash Disposal: Regular cleaning of the ash tray.
- Pellet Storage: Dry storage to maintain pellet quality.
Latest News: The U.S. Department of Energy has launched initiatives to promote the use of pellet stoves as a renewable energy source, highlighting their potential in reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
4. Catalytic Wood Stoves
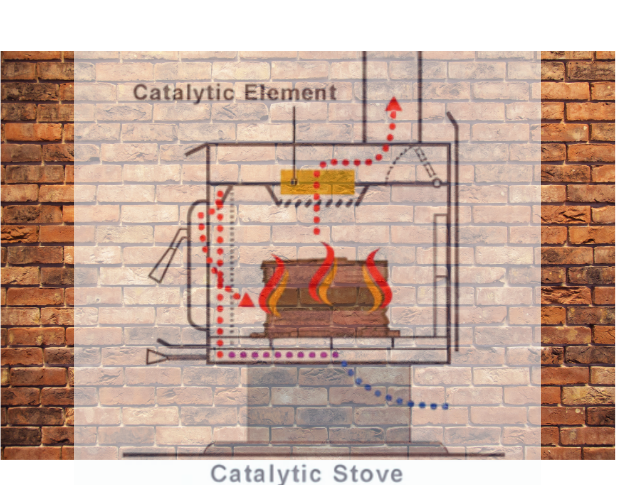
| Key Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Catalytic Combustor | Breaks down smoke particles and gases for a cleaner burn |
| Longer Burn Times | Efficient secondary combustion process |
| Environmental Benefits | Significantly fewer pollutants emitted |
Catalytic wood stoves offer high efficiency and environmental benefits.
- Use Cases:
- Perfect for homes needing long-lasting, efficient heat.
- Ideal for eco-conscious consumers.
- Installation Considerations:
- Catalytic Converter Care: Regular maintenance for optimal performance.
- Cost: Higher upfront cost due to advanced technology.
- Maintenance:
- Catalytic Combustor Cleaning: Regular cleaning and eventual replacement.
- Chimney Cleaning: Annual inspections to prevent creosote buildup.
Resource: Refer to the EPA’s list of certified catalytic wood stoves for environmentally friendly options.
5. Non-Catalytic Wood Stoves
| Key Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Simple Design | Fewer components, less maintenance |
| Moderate Efficiency | Less efficient than catalytic models but still effective |
Non-catalytic wood stoves provide a simpler, reliable heating solution.
- Use Cases:
- Great for homeowners seeking low-maintenance, reliable heating.
- Ideal for those not wanting to maintain a catalytic combustor.
- Installation Considerations:
- Less Maintenance: Simpler design means less upkeep.
- Slightly Lower Efficiency: More frequent refueling may be necessary.
- Maintenance:
- Air Tubes and Baffles: Regular cleaning for optimal performance.
- Shorter Burn Times: More frequent refueling, especially in colder weather.
Tip: Always check local incentives for purchasing and installing energy-efficient wood stoves.
FAQs (20 Questions)
1. How long do wood-burning stoves last?
- Up to 15-20 years with proper maintenance, with cast iron stoves being more durable.
2. Can I burn wood pellets in a regular wood stove?
- No, wood pellets require a specific pellet stove for safe and efficient burning.
3. What is the difference between catalytic and non-catalytic wood stoves?
- Catalytic stoves use a catalyst for a secondary burn, offering higher efficiency and longer burn times, whereas non-catalytic stoves rely on a simpler secondary combustion system.
4. How often should I have my chimney inspected?
- At least once a year, especially with regular use, to prevent creosote buildup.
5. What are EPA-certified wood stoves?
- Stoves meeting the EPA’s emissions standards, offering a more environmentally friendly option.
6. Can I install a wood-burning stove myself?
- Not recommended. Professional installation ensures safety and efficiency.
7. How do I maintain my wood stove’s efficiency?
- Regular cleaning, proper fuel storage, and annual chimney inspections.
8. Are wood-burning stoves safe for the environment?
- Can be, with proper use and maintenance. Look for EPA-certified stoves for reduced emissions.
9. What is the best type of wood for burning?
- Dry, seasoned hardwoods like oak and maple burn most efficiently.
10. Can I use my wood stove during a power outage?
- Only if you have a backup power source for pellet stoves or if using a traditional wood stove.
11. How do I choose the right size of wood stove for my home?
- Consider the space to be heated, insulation, and desired temperature increase.
12. Are there any local regulations I should be aware of?
- Yes, check with your local government for specific regulations on wood stove installations and emissions.
13. Can I convert my existing fireplace into a wood-burning stove?
- Possibly, with a wood-burning stove insert, but consult a professional first.
14. How do pellet stoves compare to traditional wood stoves in terms of cost?
- Pellet stoves can be more expensive upfront but offer long-term savings through efficiency.
15. What safety features should I look for in a wood stove?
- Look for features like overheat protection, secure door latches, and a sturdy construction.
16. Can I burn other materials in my wood stove, like coal or trash?
- No, burning unauthorized materials can be dangerous and harmful to the environment.
17. How often should I clean my wood stove?
- Regularly, with daily ash removal and deeper cleaning every 1-3 months.
18. Are there any health concerns associated with wood stoves?
- Yes, poor maintenance or improper use can lead to indoor air quality issues.
19. Can I use a wood stove as my primary heat source?
- Yes, but ensure it’s sized correctly for your space and consider backup options.
20. Are there any incentives for purchasing an energy-efficient wood stove?
- Yes, check with local and national governments for available incentives and rebates.
Conclusion
Choosing the right wood-burning stove involves understanding your heating needs, home design, and desired maintenance level. From traditional free-standing stoves to advanced pellet and catalytic models, each type offers unique benefits. By exploring the pros and cons outlined here, you can make an informed decision for your home.
Additional Resources
- EPA’s Wood Heater Emissions Standards: For the latest on environmentally friendly wood stove options.
- NFPA’s Fireplace and Chimney Safety Tips: Essential guidelines for safe installation and maintenance.
- U.S. Department of Energy’s Renewable Energy Initiatives: Explore incentives and programs supporting the use of pellet stoves and other renewable energy sources.
Online Communities:
- Wood Stove Forum for discussions and advice from experienced users.
- Renewable Energy Subreddit for exploring broader sustainable energy solutions.
Professional Assistance:
- National Chimney Sweep Guild (NCSG) for certified chimney sweeps.
- Hearth, Patio & Barbecue Association (HPBA) for finding qualified wood stove professionals.


